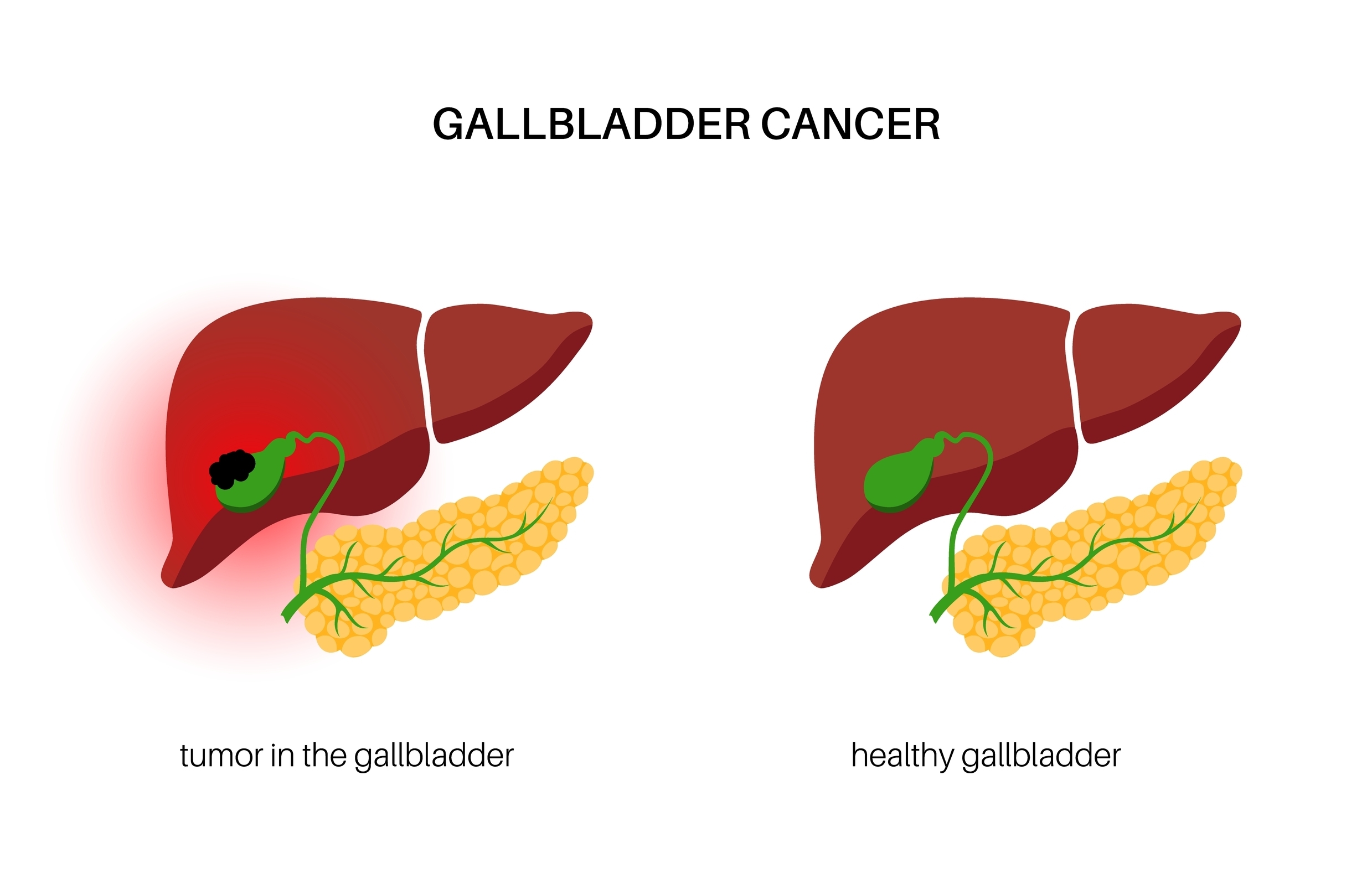
Understanding Gallbladder Cancer: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Gallbladder cancer is an uncommon but aggressive cancer that originates in the gallbladder—a small, pear-shaped organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, a fluid produced by the liver to aid digestion, and is an important part of the digestive system.
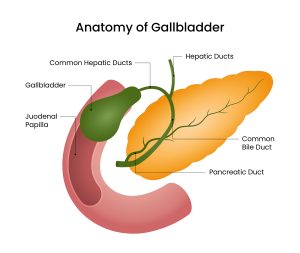
What Is Gallbladder Cancer?
Gallbladder cancer occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the tissues of the gallbladder. Most gallbladder cancers begin in the glandular cells lining the inner surface of the gallbladder. Over time, these cells can invade deeper layers and spread to nearby organs and distant sites, making early detection vital.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Cancer:
Due to its lack of symptoms, early-stage gallbladder cancer is often discovered by accident during surgery. Sometimes, there are signs, but they aren’t always clear and can be caused by other gallbladder problems. The gallbladder cancer symptoms are:
- Abdominal Pain: Continuous pain, mainly in the upper right abdomen.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Digestive discomfort and nausea.
- Jaundice: Skin and eyes yellow from bile duct blockage.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Excessive weight loss without any clear cause.
- Lump in the Abdomen: A noticeable mass in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen.
- Loss of Appetite: Loss of interest in eating.
- Dark Urine and Pale Stools: Stool and urine colour changes are brought on by disruptions in bile flow.
Risk Factors for Gallbladder Cancer:
Although the actual cause of gallbladder cancer is unknown, various risk factors enhance the likelihood of developing the disease:
- Gallstones: Chronic inflammation caused by gallstones (Cholelithiasis) is one of the most significant risk factors.
- Gallbladder Polyps: Benign growths in the gallbladder can occasionally turn cancerous.
- Age and Gender: Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and occurs more frequently in women.
- Obesity: Excess body weight can contribute to gallbladder issues, increasing cancer risk.
- Chronic Infections: Conditions like typhoid infection can elevate the risk.
- Family History: A family history of gallbladder cancer or related conditions may increase susceptibility.
- Porcelain Gallbladder: One rare but important risk factor is calcification of the gallbladder wall.
- Abnormal pancreaticobiliary anatomy and congenital biliary cysts.
- Environmental factors like certain medications, smoking, high carbohydrate intake, and harmful work exposure.
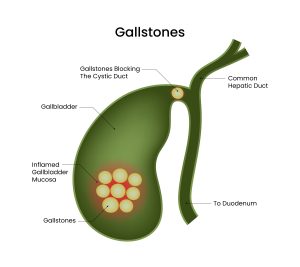
Gallstones
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Cancer:
The diagnosis of gallbladder disease involves the following methods:
- Imaging Tests:
- Ultrasound: Identifies abnormalities in the gallbladder.
- CT Scan or MRI: Generates detailed images to determine tumour size and spread.
- PET Scan: Detects cancer activity throughout the body.
2. Blood Tests:
- Liver function tests and tumour markers can provide clues about gallbladder health.
3. Endoscopic Tests:
- Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS): Provides detailed imaging of the bile ducts and gallbladder.
- ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography): Detects blockages and allows tissue sampling.
4. Biopsy:
- A tissue sample is collected for microscopic examination to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
5. Diagnostic laparoscopy:
- The doctor inserts a laparoscope, a thin tube with a camera, under the belly button to examine the area. You’ll be put to sleep for the procedure.
Treatment Options for Gallbladder Cancer:
The treatment methods for gallbladder cancer are:
- Surgery
- Cholecystectomy: The gallbladder is removed by surgery performed for early-stage cancer.
- Extended Surgery: For more advanced cases, surrounding tissues and lymph nodes may also be removed.
2. Radiation Therapy
High-energy rays target and destroy cancer cells. To improve outcomes, physicians often combine radiation with other treatments.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy kills cancer cells with drugs that are called cytotoxic. The drugs move through the body in the bloodstream.
4. Targeted Therapy
As a way to treat cancer, targeted therapy uses drugs or other substances that go after particular molecules and pathways that help cancer cells grow, spread, and become more advanced.
Boosts the immune system’s ability to fight cancer cells.

Prevention of Gallbladder Cancer:
Certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Manage Gallstones
- Adopt a Healthy Diet
- Quit Smoking
- Stay Vigilant
Conclusion:
Gallbladder cancer may seem like a very complicated medical condition at first. Still, many people have had excellent outcomes thanks to early disease detection and improvements in available treatments. As odd as it may appear, we at Omega Hospitals are committed to helping each of our patients with the best end results possible. Do not hesitate to contact your doctors if you or a family member develops clinical signs of gallbladder cancer. Timely and appropriate treatment provides the best results for these patients.
For more information or to schedule a consultation, contact Omega Hospitals today. Together, we can make strides toward better health and hope for a brighter future.