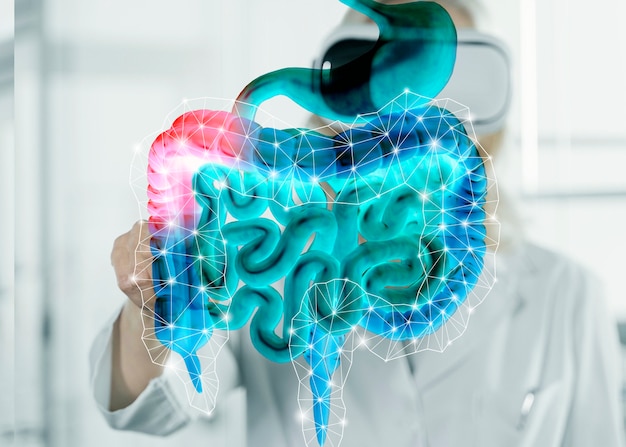
Colon Cancer Awareness: Key Signs and Symptoms You Should Never Ignore
The growth of colon cancer cells starts in the colon, a section of the large intestine. The first and longest segment of the big intestine is called the colon. The last segment of the digestive system is the large intestine. Food is broken down by the digestive system and used by the body.
Colon cancer can occur in any age group, but it usually strikes older persons. Usually, it starts off as little cell clusters inside the colon called polyps. Although most polyps are benign, some may eventually develop into colon cancer.
Polyps frequently show no symptoms. Doctors advise routine screening tests to check for colon polyps because of this. Polyp detection and removal aids in the prevention of colon cancer.
Many treatments are available to help control colon cancer if it does arise. Chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy are medical interventions used as treatments.
Occasionally, colorectal cancer is used to refer to colon cancer. In this context, rectal cancer—which starts in the rectum—is combined with colon cancer.
-
Colon Cancer Signs and Symptoms:
During the early stages, colon cancer frequently progresses slowly and may not exhibit any symptoms. The signs and symptoms of colon cancer are as follows:
Changes in Bowel Habits:
- Persistent diarrhoea or constipation.
- A change in the consistency or shape of the stool (e.g., narrow or ribbon-like stool).
- Feeling that the bowel does not completely empty after a bowel movement.
Rectal Bleeding or Blood in the Stool:
- Bright red or dark red blood in stool.
- Stool that appears dark or tar-like due to digested blood.
Unexpected Loss of Weight:
- Significant and unintended weight loss without changes in diet or exercise.
Abdominal Discomfort:
- Cramping, gas, or pain in the abdomen.
- Bloating or a feeling of fullness.
Fatigue and Weakness:
- Feeling unusually tired or weak may be due to anaemia from blood loss.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia:
- Pale skin and unexplained fatigue due to low iron levels.
Nausea or Vomiting:
- Especially if accompanied by abdominal discomfort or bloating.
Feeling of Incomplete Evacuation:
- A continuous urge to have a bowel movement even after going to the bathroom.
Symptoms of Advanced Disease:
- If cancer has spread, symptoms can be jaundice, swelling in the limbs, and difficulty breathing.
2. Screening and Early Detection of colon cancer-
- Screening Tests: Colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy, and stool-based tests can help detect colon cancer early.
- Risk Factors: Age (over 50), family history, personal history of polyps or inflammatory bowel disease, high-fat diet, smoking, and alcohol use increase the risk.
When to See a Doctor:
If you or someone you know regularly experiences any of these symptoms or is more susceptible because of a family history or other circumstances, it’s important to speak with a healthcare provider for a more thorough assessment.
Key Information:
- One kind of cancer that develops in the tissues of the colon is called colon cancer.
- One’s medical history influences the chance of getting colon cancer.
- Changes in bowel habits or blood in the stool can detect colon cancer.
- Colon cancer is diagnosed via tests that look at the colon and the rectum.
- Imaging studies are done to identify if cancerous cells have spread from the colon to other body parts after the diagnosis of colon cancer.
- Few patients prefer to take a second opinion.
Reference:
https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/colon-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20353669
https://www.cancer.gov/types/colorectal/patient/colon-treatment-pdq#_93