Oral Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
Oral cancer, commonly known as mouth cancer, can impact any mouth area, such as the lips, tongue, gums, or cheeks.
Mouth cancer can strike anyone, but as people age, their risk increases. Generally, a diagnosis is made between the ages of 66 and 70.
The type of oral cancer, its size, whether it has spread, and your overall health all affect how serious it is.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Oral cancer is strongly associated with certain risk factors, including:
- Tobacco use: Smoking cigarettes, cigars, pipes, or using chewing tobacco significantly increases the risk.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy alcohol use can increase the risk of oral cancer, especially when combined with tobacco use.
- HPV infection: Infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV-16, has been linked to a subset of oral cancers.
- Sun exposure: Excessive sun exposure to the lips can increase the risk of lip cancer.
- Age and Gender: Oral cancer is more common in people over the age of 40 and is more prevalent in men than in women.
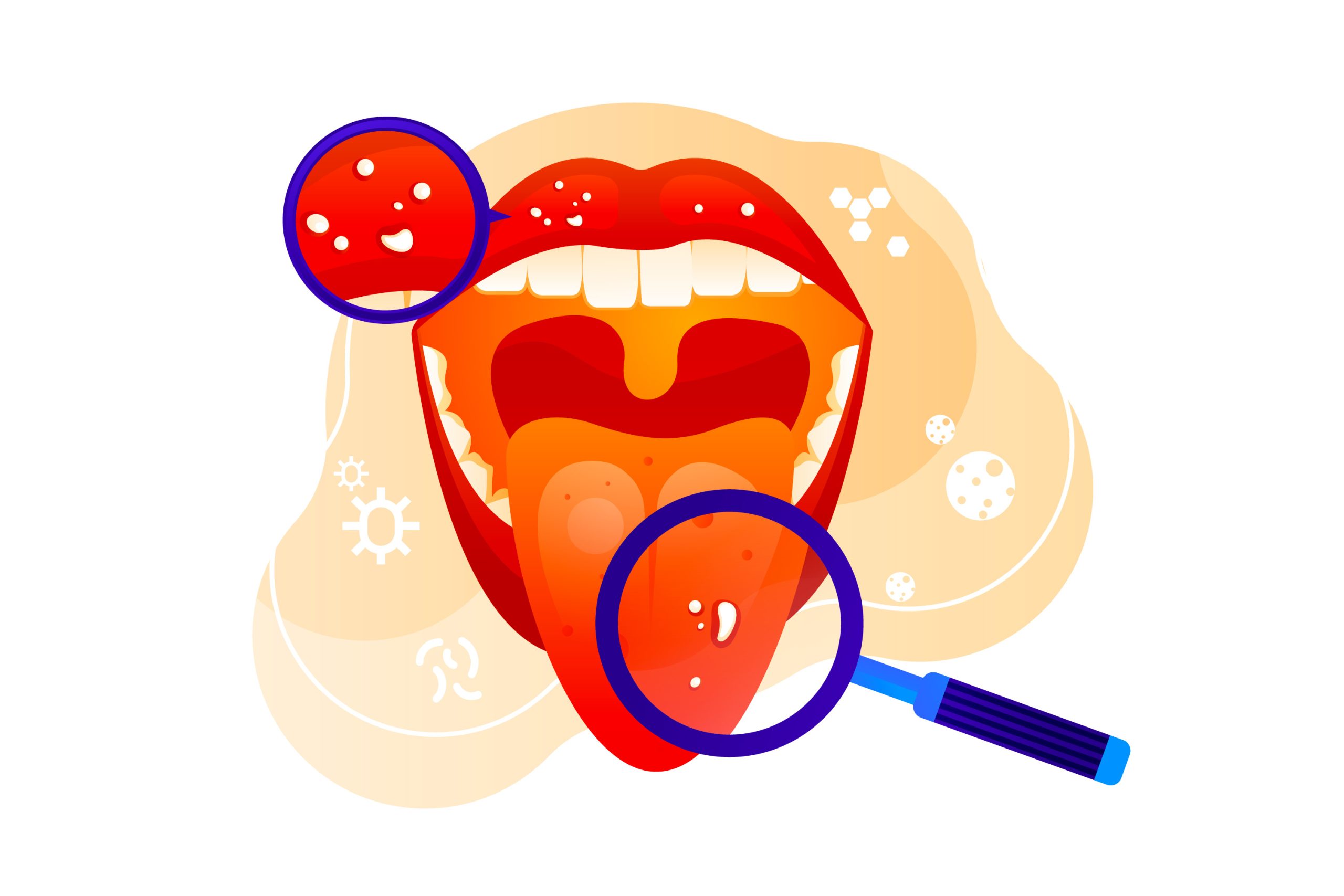
Symptoms of oral cancer can vary but often include the following signs:
- Sores and Ulcers: Persistent sores in the mouth that do not heal within two weeks and often bleed easily.
- Lumps or Thickening: Lumps, bumps, or rough spots, as well as thickening of the tissues inside the mouth.
- White or Red Patches: Unexplained white or red patches on the gums, tongue, tonsil, or lining of the mouth.
- Pain and Tenderness: Pain, tenderness, or numbness anywhere in the mouth or on the lips.
- Difficulty Chewing or Swallowing: Challenges in chewing, swallowing, speaking, or moving the jaw or tongue.
- Jaw Issues: Swelling of the jaw that causes dentures to fit poorly or become uncomfortable.
- Teeth Changes: Loose teeth with no apparent dental cause.
- Persistent Sore Throat: A feeling that something is caught in the throat or a persistent sore throat.
- Voice Changes: Changes in the voice or a chronic hoarseness.
If you experience any of these symptoms persistently, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider as early as possible for evaluation, as early detection significantly improves the outcomes of oral cancer treatment.
Diagnosis:
Diagnosis of oral cancer involves a physical examination, which may include using a small mirror and a light to look at the roof and back of the mouth, as well as the throat. A biopsy of any abnormal area is typically performed to confirm cancer.
Treatment:
Treatment options vary based on the stage of the cancer and may include surgery to remove the cancerous growth, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of treatments. Regular dental visits can help catch oral cancer early, potentially making treatment easier and more effective.