Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Risk Factors, Prevention, Diagnosis, Treatment
Cancer that originates in the lungs is known as Lung cancer. Lungs are exposed to a lot of toxic substances we inhale, such as pollution or tobacco; that’s why lung cancer is so common. The majority of cancer-related deaths worldwide occur due to lung cancer, with the highest mortality rates among both men and women.
Symptoms:
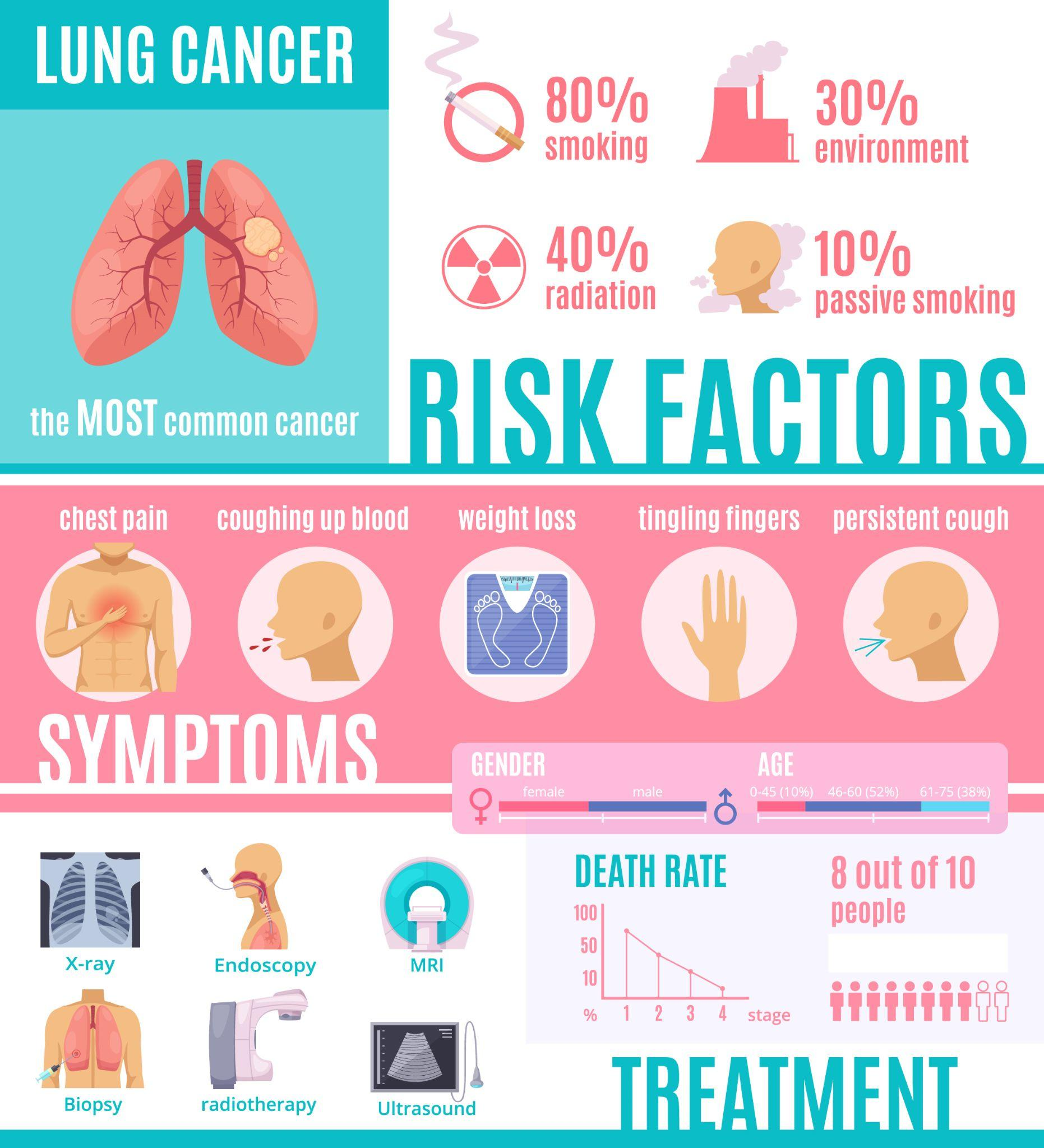
- Cough with occasional blood in sputum.
- Chest pain
- Breathlessness
- Hoarseness of voice
- Facial puffiness and dilatation of veins over chest and neck.
- Back pain, headache, seizures in case of metastatic disease.
Risk factors:
- Smoking is the most important risk factor for the development of lung cancer, accounting for 90% of the cases. Another major contributor to lung cancer is secondhand smoke. Tobacco smoke contains nearly 70 cancer-causing substances (carcinogens). In India, the most common tobacco products are cigarettes, gutkha, khaini, zarda, etc. Smoking also causes oral, throat, oesophagal, stomach, colorectal and bladder cancers.
- Occupational exposure to asbestos, arsenic, chromium, beryllium, nickel, soot, or tar.
- Exposure to radiation
- Hereditary factors
- Radon gas exposure in the home or workplace.
- Air pollution: exposure to diesel exhaust is associated with an increased risk of lung cancer.
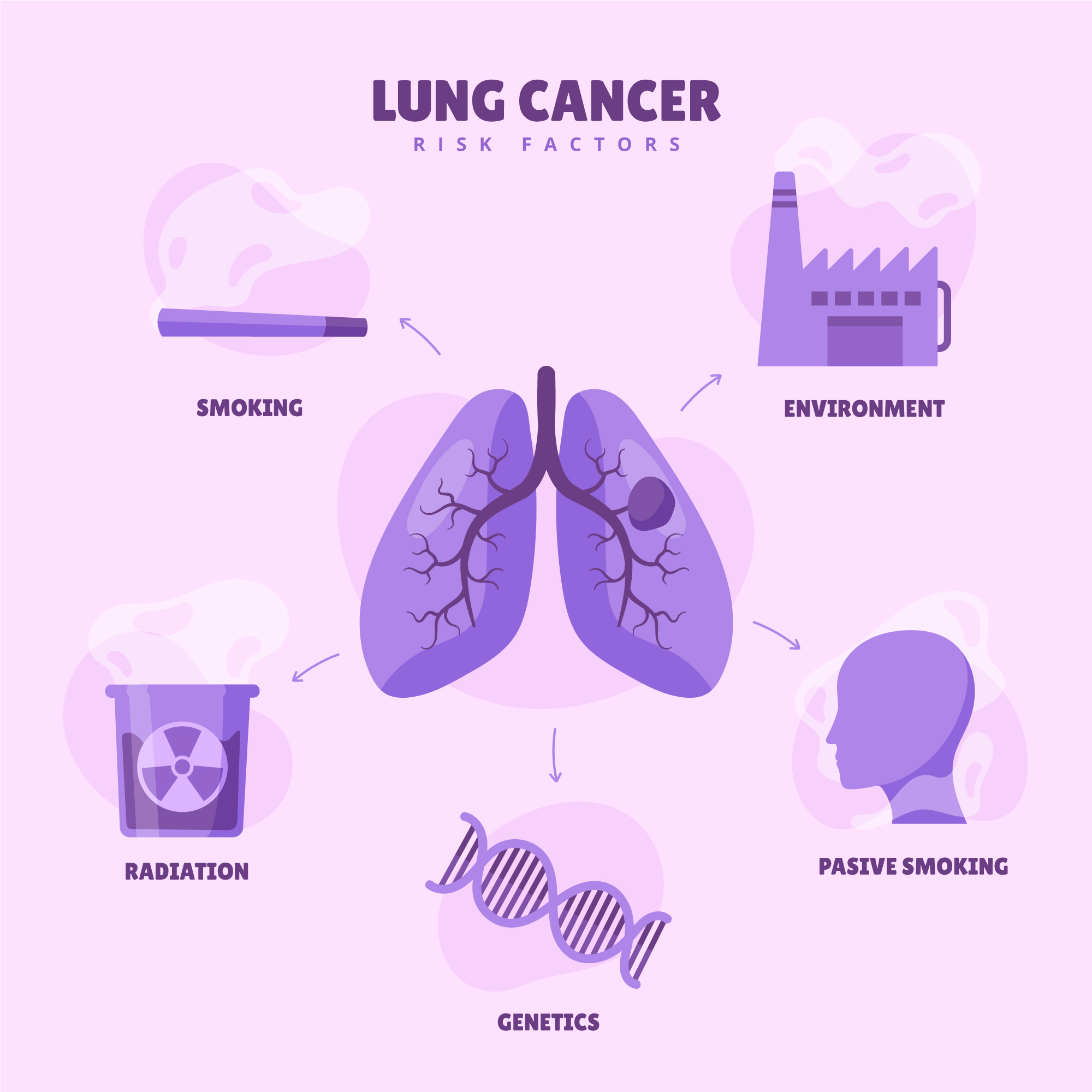
Lung Cancer Risk Factors
Lung cancer prevention:
Lung cancer might be prevented by following the below-given measures:
- Quit Smoking
- Avoid Secondhand Smoke
- Radon Testing
- Limit Exposure to Carcinogens
- Healthy Diet
- Regular Exercise
- Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Take Vitamin Supplements
- Early cancer screening
Lung Cancer diagnosis:
The standard method for diagnosing lung cancer involves a review of medical history, physical examination, imaging tests, and laboratory work.
The standard procedures for diagnosing lung cancer are listed below.
- Medical History: The physician will start by gathering a comprehensive medical history, which includes asking about your symptoms, risk factors (such as smoking history), and any family history of cancer.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination could be done to detect any physical signs or symptoms that are related to lung cancer, such as wheezing, coughing, or chest pain.
- Imaging Tests: These tests are often used to visualise the lungs and detect abnormalities. Standard imaging tests for lung cancer include:
- Chest X-ray: Provides a basic view of the lungs.
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: Offers a more detailed and 3D view of the lungs, helping to identify the size, location, and extent of tumours.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan: This can help determine if lung cancer has metastasised to other body parts.
- Biopsy: A biopsy is usually necessary to confirm lung cancer and identify its specific type. A pathologist uses a microscope to examine a sample of tissue taken from the lung during a biopsy.
- Bronchoscopy: A medical procedure called a bronchoscopy is used to look inside the lungs and airways. A trachea (windpipe) and bronchial tubes are reached through the mouth or nose, and a thin, flexible tube called a bronchoscope is used for the procedure. Both therapeutic and diagnostic uses are possible for bronchoscopy procedures.
- Molecular Testing: In cases where lung cancer is confirmed, molecular testing may be conducted to determine specific genetic mutations or biomarkers. This information helps guide treatment decisions, such as targeted therapies.
- Staging: Lung cancer is staged to determine the extent of its spread upon diagnosis. This assists doctors in planning the most appropriate treatment.
Lung Cancer Diagnosis
Types of Lung Cancer:
There are two most common kinds of lung cancers: These two forms do not grow identically and have different treatments
- Small cell lung cancer
- Non-small cell lung cancer (the most frequent)
Small-cell lung cancer: It is more severe than large-cell lung cancer because it cannot be detected early, and it is mostly diagnosed after the disease has spread to other organs. There are three major types of small-cell lung cancer:
- Small cell carcinoma
- Mixed small-cell/large cell
- Combined small cell carcinoma
Non-small cell lung cancer – It is the most common type, accounting for the majority of cases (80-85%), and grows slowly when compared to SCLC.
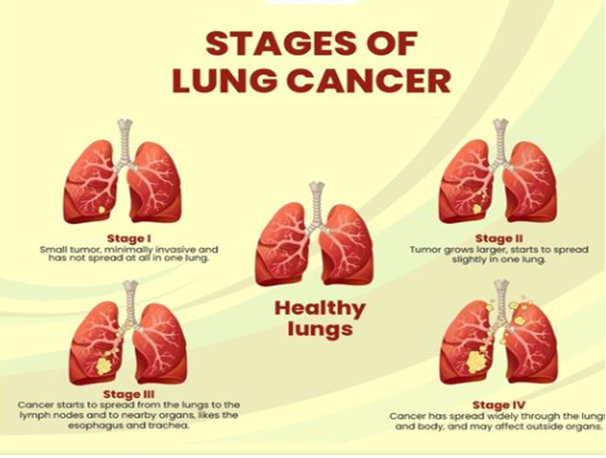
Stages of Lung Cancer
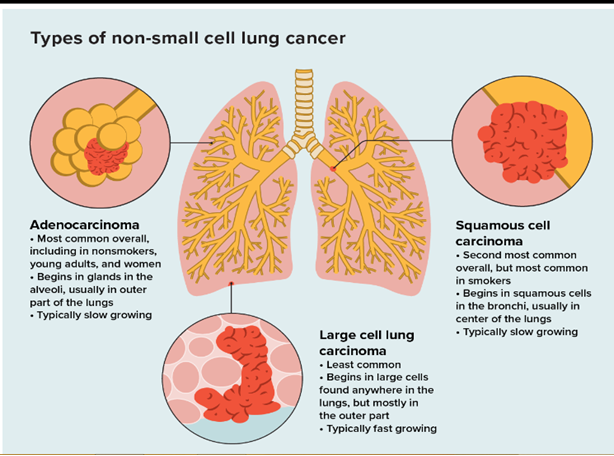
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung Cancer Treatment:
Treatment is based on the type of cancer, molecular profiling, how much it has spread, patient comorbidities and performance status.
- Surgery: The primary treatment for early-stage lung cancer (i.e. tumour limited to the lung, without spreading to other organs or lymph nodes) is surgical removal of the tumour through procedures such as lobectomy, segmentectomy, or wedge resection. In cases where surgery is not feasible, radiation therapy or stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) may be used as the primary treatment.
- Wedge resection: To eliminate a small portion of the lung that contains the tumour and a portion of healthy tissues.
- Segmental resection: To eliminate a major part of the lung, but not an entire lobe.
- Lobectomy: To take out the entire lobe of one lung.
- Pneumonectomy: To remove an entire lung.
- Radiotherapy: Radiation therapy, or radiotherapy, targets and destroys or shrinks cancer cells using high-energy radiation.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment modality as the majority of lung cancer patients present in the advanced stages where surgery and radiotherapy are not helpful. It involves using drugs circulating throughout the body to kill cancer cells.
- Target therapy: Target therapy targets the genes and proteins associated with that particular cancer, stopping the growth and spread of cancer cells while causing minimal damage to healthy, normal cells.
- Immunotherapy: The body’s immune system is utilised to recognise and fight cancer cells, a form of cancer treatment.
- Photodynamic therapy (PDT): In photodynamic therapy (PDT), a photosensitive drug and a specific light are employed to treat various medical conditions, including cancer and certain skin conditions.
Lung Cancer
Looking for high-quality and affordable medical treatment?
Choose Omega Hospitals for the best and most affordable cancer treatment
With a team of skilled medical professionals and advanced equipment, Omega Hospitals is dedicated to providing the best possible care to patients.