Esophageal Cancer Explained: From Early Symptoms to Advanced Treatment Options
Esophageal cancer, a serious malignancy of the esophagus, the long tube that carries food from your throat to your stomach, is a significant health challenge worldwide. While it may not be as commonly discussed as other forms of cancer, understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early detection and effective management. This comprehensive guide will explore the key aspects of esophageal cancer to raise awareness and provide valuable insights for those affected by or at risk of this disease.
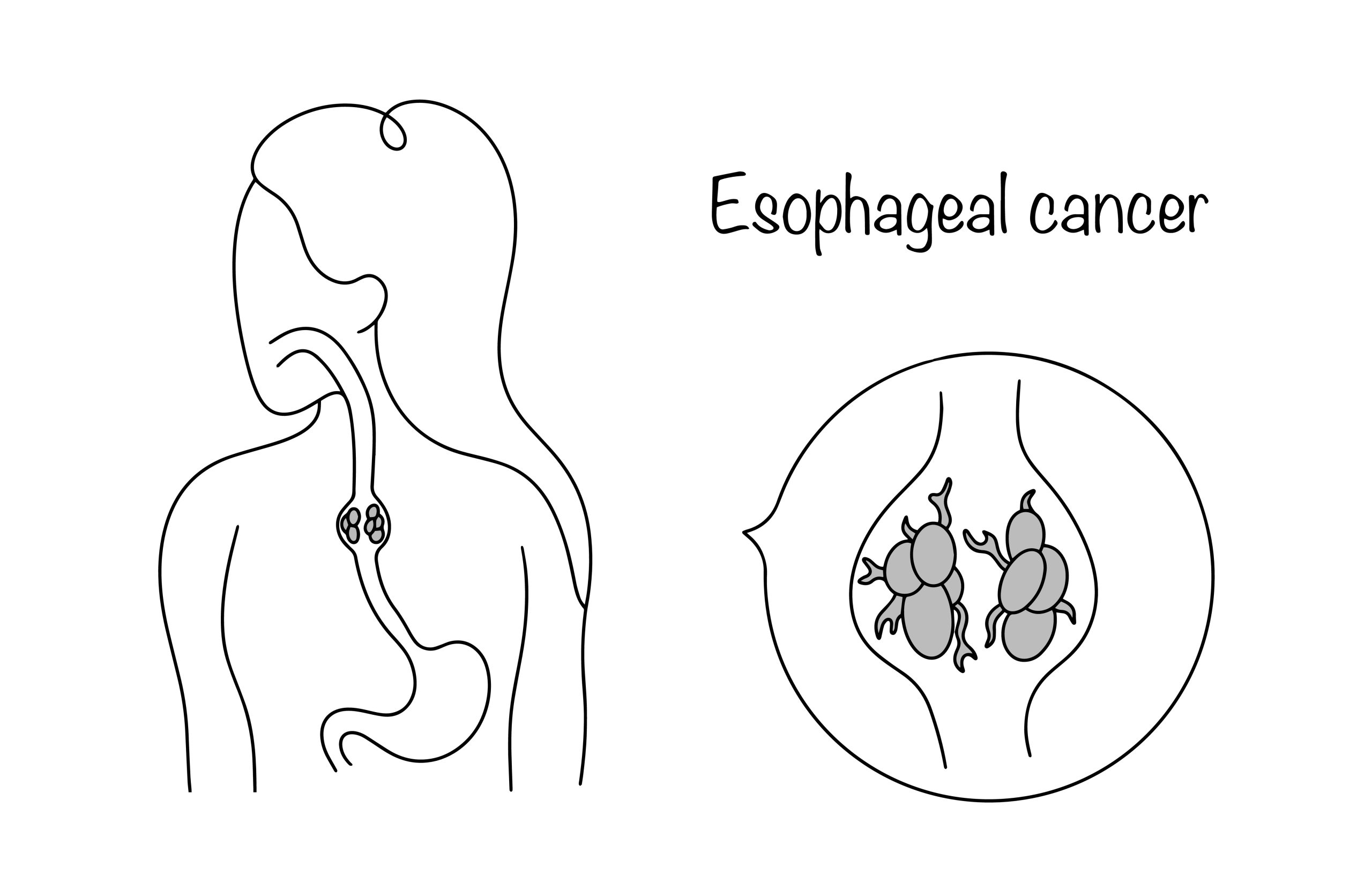
What is Esophageal Cancer?
Esophageal cancer starts in the cells of the esophagus. There are two main types of esophageal cancer, categorized based on the type of cells that are involved. The first type is esophageal adenocarcinoma, which begins in the cells of mucus-secreting glands in the esophagus. The second type, squamous cell carcinoma, originates in the flat, thin cells lining the esophagus. These two types have different causes and risk factors.
Causes and Risk Factors of Esophageal Cancer:
The exact cause of esophageal cancer is not fully understood, but several risk factors have been identified that increase the likelihood of developing this disease:
- Chronic acid reflux (GERD): Gastroesophageal reflux disease, or GERD, can lead to changes in the lower esophagus that may result in adenocarcinoma.
- Tobacco use: Smoking or chewing tobacco significantly increases the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking can increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Poor nutrition: Diets low in fruits and vegetables can increase your risk.
- Obesity: Being overweight can increase the risk of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus.
- Barrett’s esophagus: A condition in which the tissue lining the lower esophagus changes due to repeated exposure to stomach acid, significantly increasing the risk of adenocarcinoma.
Symptoms:
Esophageal cancer tends to be asymptomatic in its early stages. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include:
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): This is often one of the first symptoms.
- Weight loss: Unintentional weight loss without trying is a common sign of many forms of cancer, including esophageal cancer.
- Chest pain or discomfort: Often felt behind the breastbone.
- Indigestion or heartburn: Persistent or worsening.
- Coughing or hoarseness: Symptoms due to the tumor affecting the throat.
Diagnosis:
Early detection of esophageal cancer can significantly improve the outcome. The following methods are commonly used for diagnosis:
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a light and camera (endoscope) is passed down your throat to examine the inside of your esophagus.
- Biopsy: During an endoscopy, a doctor may remove a sample of tissue for lab testing to determine the presence of cancer cells.
- Imaging tests: Techniques such as CT scans, PET scans, or MRIs can help determine the extent (stage) of the cancer.
Treatment Options:
Treatment for esophageal cancer depends on many factors, including the stage of the cancer, the overall health of the patient, and the type of cancer (adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma). The main treatments include:
- Surgery: Removal of the tumour and some surrounding healthy tissue.
- Radiation therapy: Uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Focuses on specific weaknesses present within cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Helps your immune system fight cancer.
Prevention:
While not all cases of esophageal cancer can be prevented, certain lifestyle changes can reduce the risk:
- Avoid tobacco: Both smoking and chewing tobacco significantly increase your risk.
- Limit alcohol: Reducing alcohol consumption can lower your risk of squamous cell carcinoma.
- Eat a healthy diet: A diet rich in fruits and vegetables can help lower your risk.
- Maintain a healthy weight: This can reduce your risk of adenocarcinoma.
Living with Esophageal Cancer:
Living with esophageal cancer can be challenging, but managing your condition with the help of a specialized healthcare team can improve your quality of life. It’s also important to seek support from friends, family, or support groups who can offer the emotional and practical support needed during this time.
Conclusion:
Esophageal cancer is a complex disease with multiple facets, from risk factors and symptoms to treatments. Awareness and understanding are critical for early detection and effective treatment. If you have risk factors or symptoms associated with esophageal cancer, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider who can guide you based on the latest medical protocols and treatments. With advancements in medical science, the outlook for esophageal cancer patients is improving, offering hope and improved outcomes.